Introduction
Feasibility Report For Aquaponic Farming .
Aquaponics Farming is a food production technique that combines hydroponics (water-based plant growing) and aquaculture (tank-based raising of aquatic organisms such as fish, crayfish, snails, and prawns) by supplying nutrient-rich aquaculture water to hydroponically produced plants.
Although all aquaponic systems are based on current hydroponic and aquaculture farming processes, the size, complexity, and types of food produced may range significantly from any system found in a specialized agricultural discipline.


Aquaponics involves growing plants in a grow bed while maintaining fish in a tank. The nutrient-rich water from the fish tank, which contains fish waste, is fed into the grow bed, where billions of naturally occurring beneficial bacteria convert ammonia to nitrites and then nitrates.
Plants absorb nitrates and other nutrients to promote growth. The plant’s roots clean and filter the water before returning it to the fish tank, which houses the fish. The fresh, clean, and oxygenated water is recirculated back into the fish tank, and the cycle begins again.
The three main components of aquaponics are fish, plants, and microorganisms. Microbes operate as a bridge, converting fish waste into plant nutrients. Contemporary aquaponic designs fall into three categories: deep-water or “raft,” nutrient film technology (NFT), and media-based bed or reciprocating systems.

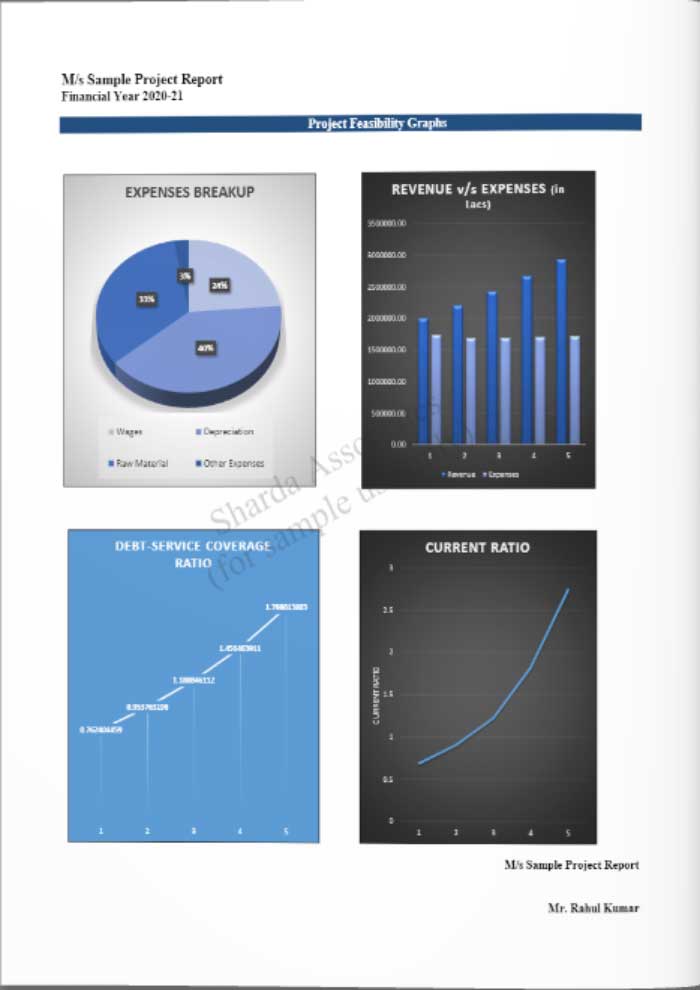
Feasibility Report Sample On Aquaponic Farming


Market Strategy of Aquaponic Farming
Aquaponics Market size was valued at USD 1.20 billion in 2021 and is poised to grow from USD 1.39 billion in 2022 to USD 4.56 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 16% in the forecast period (2023-2030). Improving urban farming methods, increasing fish consumption,
rising demand for organic fruits and vegetables, growing reduction in arable land areas, and changing climate conditions are the key factors driving the growth of the aquaponics market. Furthermore, the growing use of aquaponic systems in offices and restaurants and reducing water use and discharge to the environment are expected to provide significant growth opportunities for players operating in the market.
Aquaponics is a food-production method that combines aquaculture (the breeding of aquatic animals in tanks) and hydroponics (the growing of plants in water), in which nutrient-rich aquaculture water is delivered to hydroponically grown plants,
where nitrifying bacteria convert ammonia to nitrates. Because all aquaponic systems are based on contemporary hydroponic and aquaculture farming techniques, the size, complexity, and types of foods grown in an aquaponic system can differ just as much as any other system found in a different agricultural field. Because aquaponics is free of artificial fertilizers and crop protection chemicals, and fish waste serves as the principal nutrition for plants,
the demand for organically grown crops has huge potential & an unexplored market for emerging aquaponic farms & aquaponic system vendors.



