Feasibility Report On Medical Devices Manufacturing
Medical device manufacturing refers to the process of designing, producing, and assembling medical devices used in healthcare for diagnosis, treatment, or monitoring of patients. It involves strict quality control, adherence to regulatory standards, and ensuring safety and efficacy of the devices.
Introduction
Feasibility Report For Medical Devices Manufacturing.
Medical devices encompass a wide range of products, including medical gloves, bandages, syringes, blood pressure monitors, and X-ray equipment. They are distinct from medicines in that they either have a physical or mechanical effect on the body or are used to measure (or monitor) the body and its processes. While the goal of these items is to help you enhance your health and well-being, it’s vital to understand that they can potentially pose hazards.
Medical devices come in a wide spectrum of sophistication, from extremely sophisticated computerised medical equipment to two tongue depressors. Similarly, the World Health Organisation (WHO) defines medical devices as items whose primary mechanism of action is neither immunological, metabolic, or pharmacological in origin. Medical device manufacturing encompasses all aspects of medical device fabrication, from establishing a manufacturing process through scaling up to continual process improvements. It also comprises the sterilisation and shipping of a gadget.

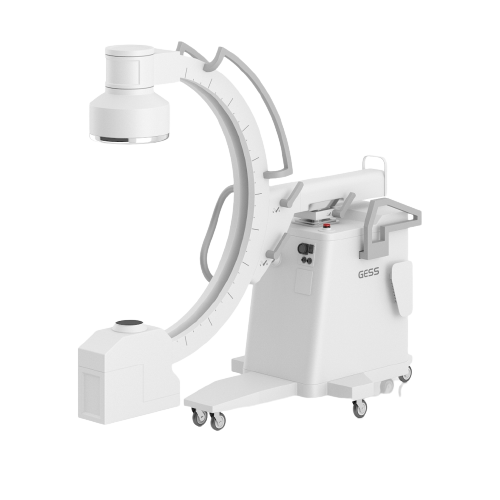
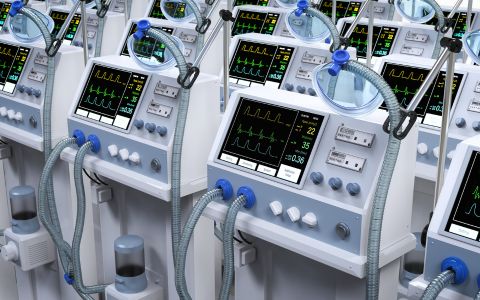
Engineers, designers, and medical specialists collaborate to provide a precise design specification. A prototype of the medical gadget is created once the design specifications have been established. During this stage, a preliminary version of the device is created to verify its functionality, usability, and safety. The prototype is rigorously tested to ensure that it meets the necessary standards and laws. Performance testing, durability testing, and safety testing may all be included. Based on the test results, any necessary tweaks or refinements are implemented. The medical device’s separate components are manufactured. Depending on the materials and complexity of the device, this may include procedures such as injection moulding, machining, extrusion, or casting.
The produced components are then put together to form the final medical gadget. Depending on the device’s complexity and production volume, this can be done manually or through automated methods. Rigid quality control methods are performed throughout the production process to guarantee that the device satisfies all regulatory standards and specifications. Inspections, testing, and validation processes at various levels may be included. Following sterilisation, the device is packaged and labelled in accordance with regulatory requirements. Packaging materials are chosen to preserve the product during storage and transit, and labelling includes important information such as the product name, instructions for use, and regulatory compliance markings.
Feasibility Report Sample On Medical Devices Manufacturing

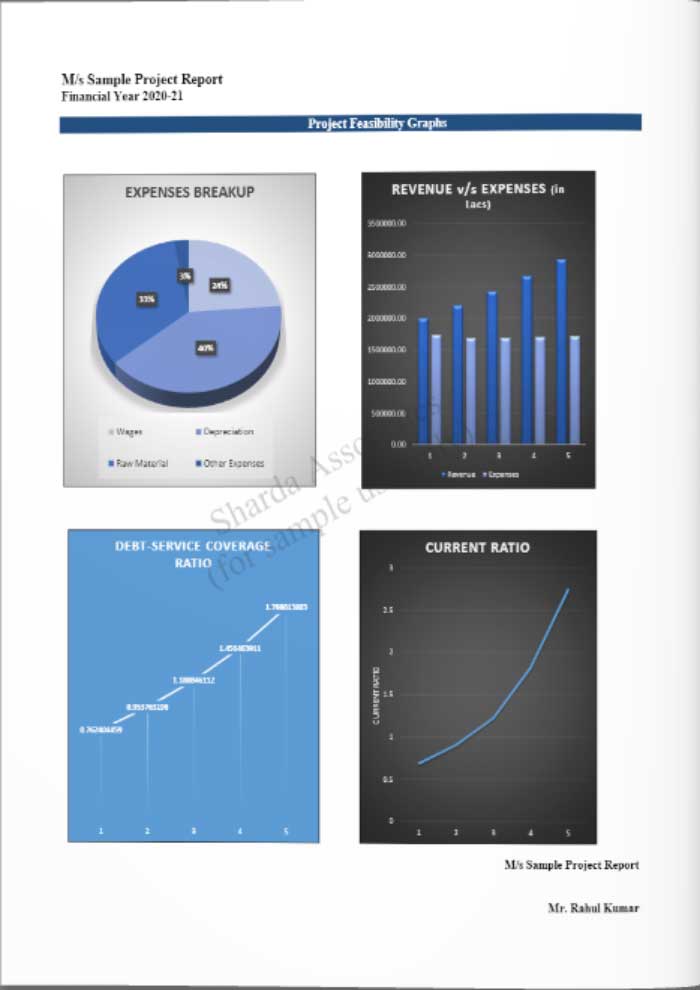

Market Strategy of Medical Devices Manufacturing
The global medical devices market was estimated at USD 512.29 billion in 2022 and is expected to increase at a CAGR of 5.9% from USD 536.12 billion in 2023 to USD 799.67 billion by 2030.
The rising incidence of chronic diseases, combined with healthcare providers’ increased emphasis on early diagnosis and treatment, is contributing to an increase in the number of patients undergoing diagnostic and surgical operations. The cardiology segment in the medical devices market is predicted to develop significantly over the forecast period due to factors such as increased prevalence of cardiovascular illnesses, strategic initiatives by leading market participants, and technical advancement in cardiology devices.
Technological advancements are accelerating the growth pace of the medical devices industry. Medical device makers have designed manufactured medical devices that are cost-effective, efficient, accurate, and can give better patient outcomes by utilising the most recent technical breakthroughs. In recent years, digital health technologies such as mHealth applications, telemedicine, and wearable medical devices, for example, have brought about numerous improvements in healthcare delivery.
Using these advancements, people can receive treatment from the comfort of their own homes by communicating with healthcare providers, resulting in effective healthcare delivery at lower healthcare costs. Increased investment in research and development by medical technology businesses, as well as favorable conditions offered by regulatory bodies for their approval, are likely to increase the medical devices market during the projection period.



