Feasibility Report on Textile Industry
The textile industry is a major provider to the country’s economy and a significant job creator. India’s textile sector is among the best in the globe, accounting for roughly 16% of overall industrial output and 33% of overall exports.
What is Textile Industry?
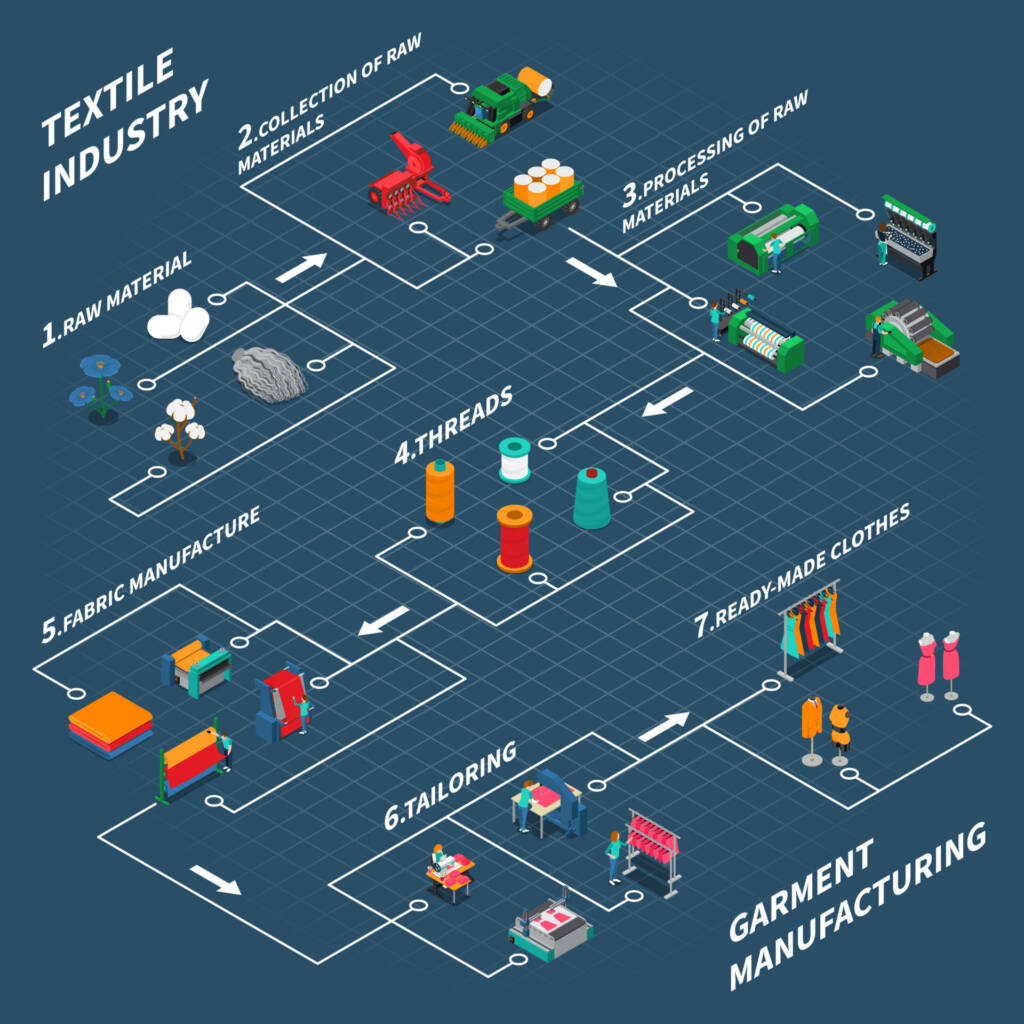
The textile industry encompasses all aspects of textile research, design, development, manufacture, and distribution. This business is increasingly diverse, with hand-spun and hand-woven textiles at one and capital-intensive modern mills at another. The dispersed powered looms/hosiery and knitting industry is the main element of the textile industry. The textile industry is capable of producing a diverse range of products appropriate for various market sectors both in India and throughout the planet.
Textile is the 2nd most fundamental requirement of humans. It does have a very large influence on our everyday lives Before the dawn of time, humans often use numerous sorts of textiles for protection, heat, personal decoration, and also to demonstrate individual status. Several other varieties of present textile fabrics, made from both natural and synthetic elements, are frequently classified as per type.
The price of fibers is influenced by their accessibility, the type and quantity of processing needed, and their flexibility. Natural fibers often need a large amount of land to be produced, are impacted by environmental circumstances, and should often be carried considerable miles to the place of manufacture.
Spinning is the process of turning fiber—natural or synthetic—into yarn. There are numerous processes in the spinning sector, including blow room, carding, drawing, combing, simplex, and ring frame. The first stage of spinning is blow room. Here, the cotton bale is opened, cleaned, blended, or mixed to create a homogeneous lap of a specific length. Carding comes next. The heart of spinning is referred to as carding. Drawing comes in third.
The slivers are combined, multiplied, levelled, and drafted in this place. After that comes combing. It is a method for parallelizing and straightening fibers while also removing short fibers and contaminants. The following step is simplex. Slivers are weakened and slightly twisted in this instance. The slivers are afterwards transformed into roving.
Feasibility Report Sample On Textile Industry


Market Strategy Of Textile Industry
India’s textiles and clothing sector are strong throughout the supply chain, from fiber to yarn to fabrics to garments. It is very broad, with a diverse variety of categories varying between traditional handloom items, handicrafts, wool and silk items, to the modern textile mills.
The organized textile industry, which encompasses spinning, weaving, processing, and garment manufacture, is distinguished by the employment of capital-intensive technologies for the mass production of textile items. In 2020-21, the local textiles and clothing sector was valued at $99.2 billion, of which $82 billion was used locally and the rest was exported to the global market.
Fabrics are created using a variety of techniques. Their main techniques are knitting and weaving. Weaving is the principal method used to create fabrics. The technique probably gained notoriety before spinning. Observing the grasses and twigs in bird nests may have taught primitive people how to make clothing for themselves. Spinning began when people realized that the basic materials might be improved before being sewn.
Extremely simple, hand-operated, primitive looms that were developed throughout time. Different contemporary looms have been invented, although they generally accomplish the same task as the straightforward hand-operated loom. Other divisions within the weaving sector include winding, warping, sizing, and looming. The second most popular way for making fabrics is knitting.
Cotton cultivation employs 6.1 million farmers as well as million individuals in connected industries. Furthermore, the $99.2 billion in domestic consumption was split into clothing, technical textiles, and home goods. While clothing exports were $13 billion, home textile exports totalled $2.3 billion, fabric exports totalled $5 billion, yarn exports totalled $2.4 billion, fibre exports totalled $1.6 billion, and others totalled $3 billion.



