Feasibility Report On Welding Rod Manufacturing
Welding Rod Manufacturing is the process of creating consumable rods used in welding operations. These rods, coated with flux, melt to join metal pieces together when heated. Vital for construction, automotive, and manufacturing sectors, the production involves material selection, coating application, and quality control, contributing to strong and durable welds.
Introduction
Feasibility Report For Welding Rod Manufacturing.
Welding is a fabrication method that causes the fusion to combine materials, typically metals or thermoplastics. This is commonly accomplished by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to generate a pool of molten material (the weld puddle) that cools to form a strong joint, but pressure can also be used in conjunction with or instead of heat to produce the weld. In contrast, soldering and brazing entail melting a lower-melting-point material between the workpieces to produce a bond without melting the workpieces themselves. Many different types of welding are produced, such as gas welding, resistance welding, energy beam welding, solid-state welding, etc.
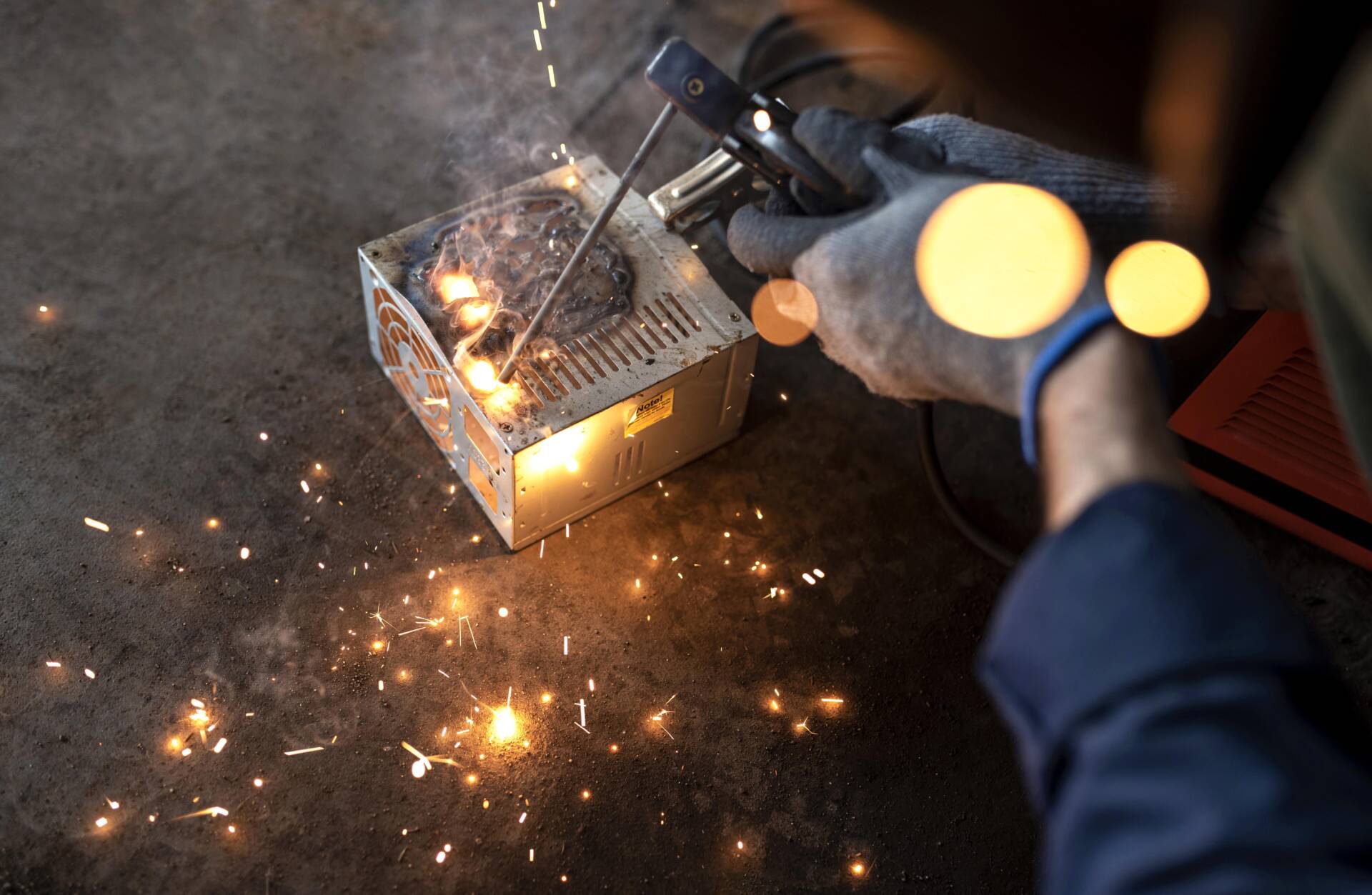
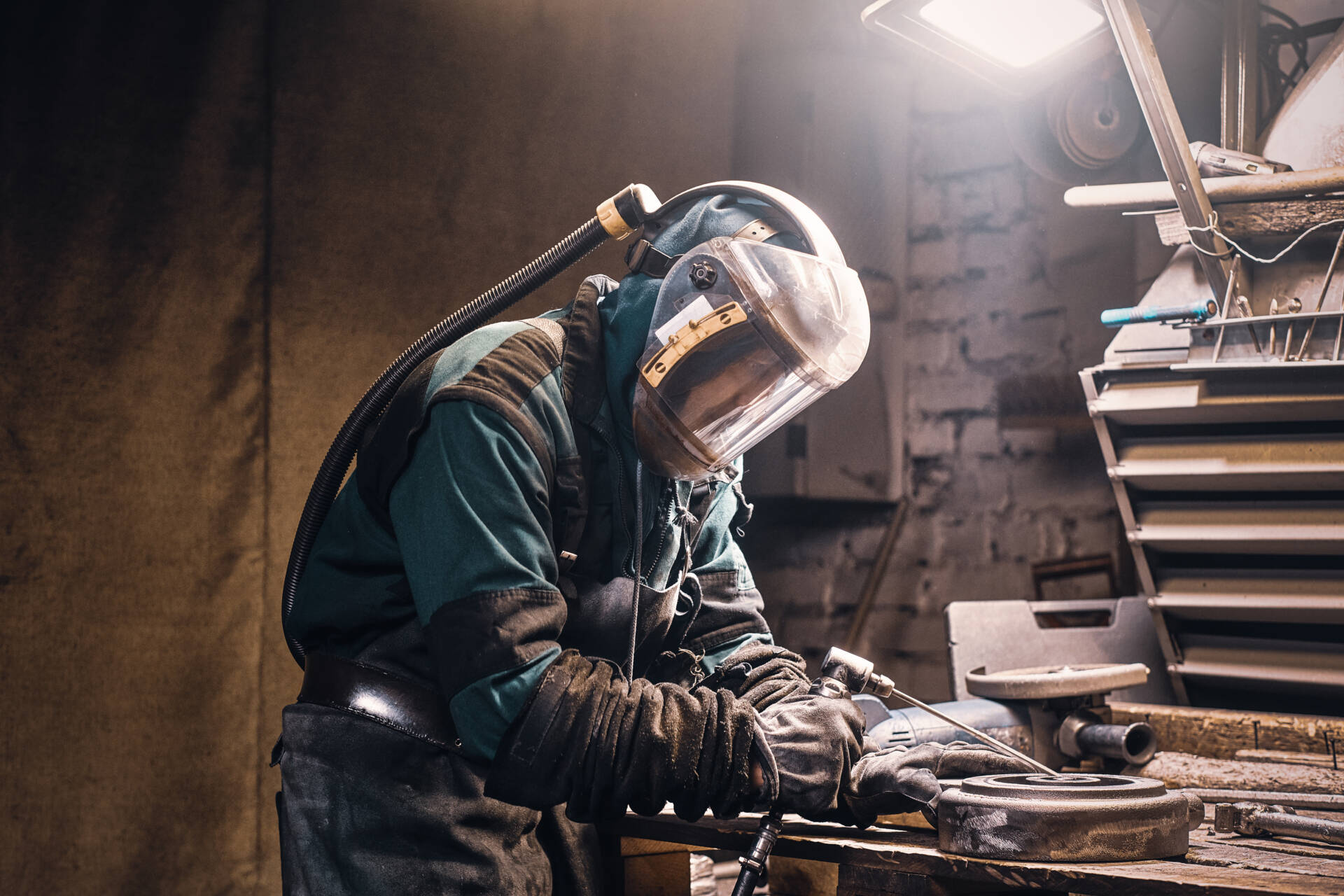


Welding can be done with a variety of energy sources, including a gas flame, an electric arc, a laser, an electron beam, friction, and ultrasound. Welding, while often an industrial procedure, can be performed in a variety of conditions, including open air, underwater, and in space. Welding remains dangerous regardless of location, and measures must be taken to avoid burns, electric shock, poisonous gases, and over exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
The use of welding rods might be either consumable or non-consumable. Consumable rods break down or melt to create the adhesive that joins two metal parts. Non-consumable rods, on the other hand, merely offer the base metals enough catalytic reaction to promote their fusing in an oxygen-rich air environment. Any continuous weld bead’s length is inversely related to the welding rod’s length.

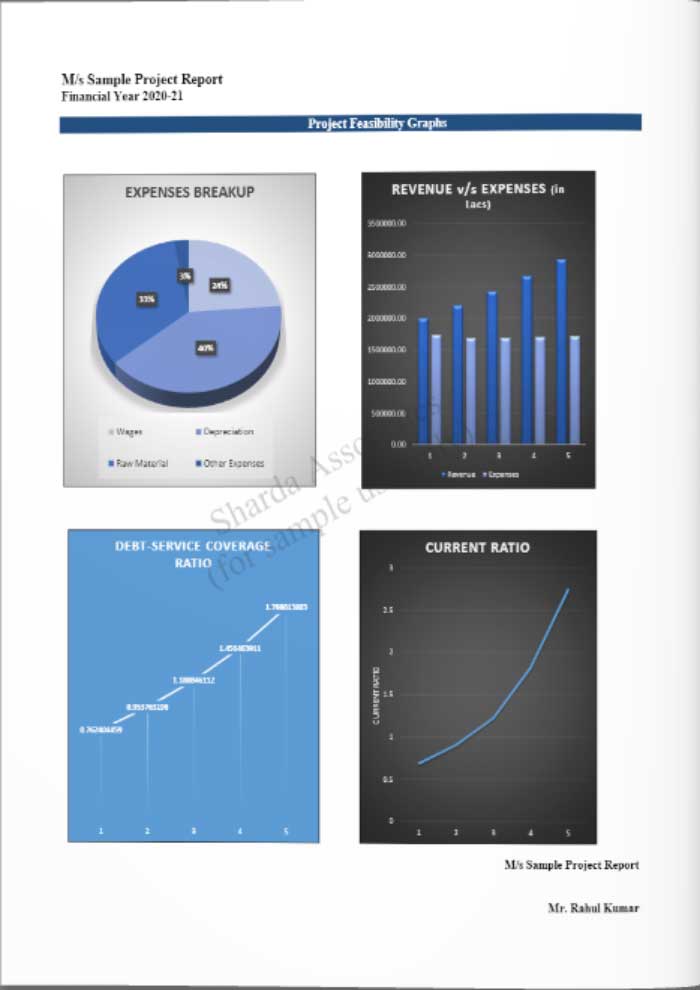
Feasibility Report Sample On Welding Rod Manufacturing


Market Strategy of Welding Rod Manufacturing
The global welding electrodes market was worth USD 3.02 billion in 2019 and is expected to be worth USD 3.79 billion by 2027, growing at a 3.0% CAGR during the forecast period.
The welding industry is currently facing issues since engineers and welders executing welding activities on the factory floor have been educated on various welding precautions and discipline, but rarely on how to carry out these operations. Furthermore, welders and engineers typically learn to weld and perform their abilities while completing welding operations, rather than through apprentices or recognized welder training. Accidents are more likely to occur in this scenario because the user is unaware of aspects such as the time required to heat the metals, the supply of required current, and others.
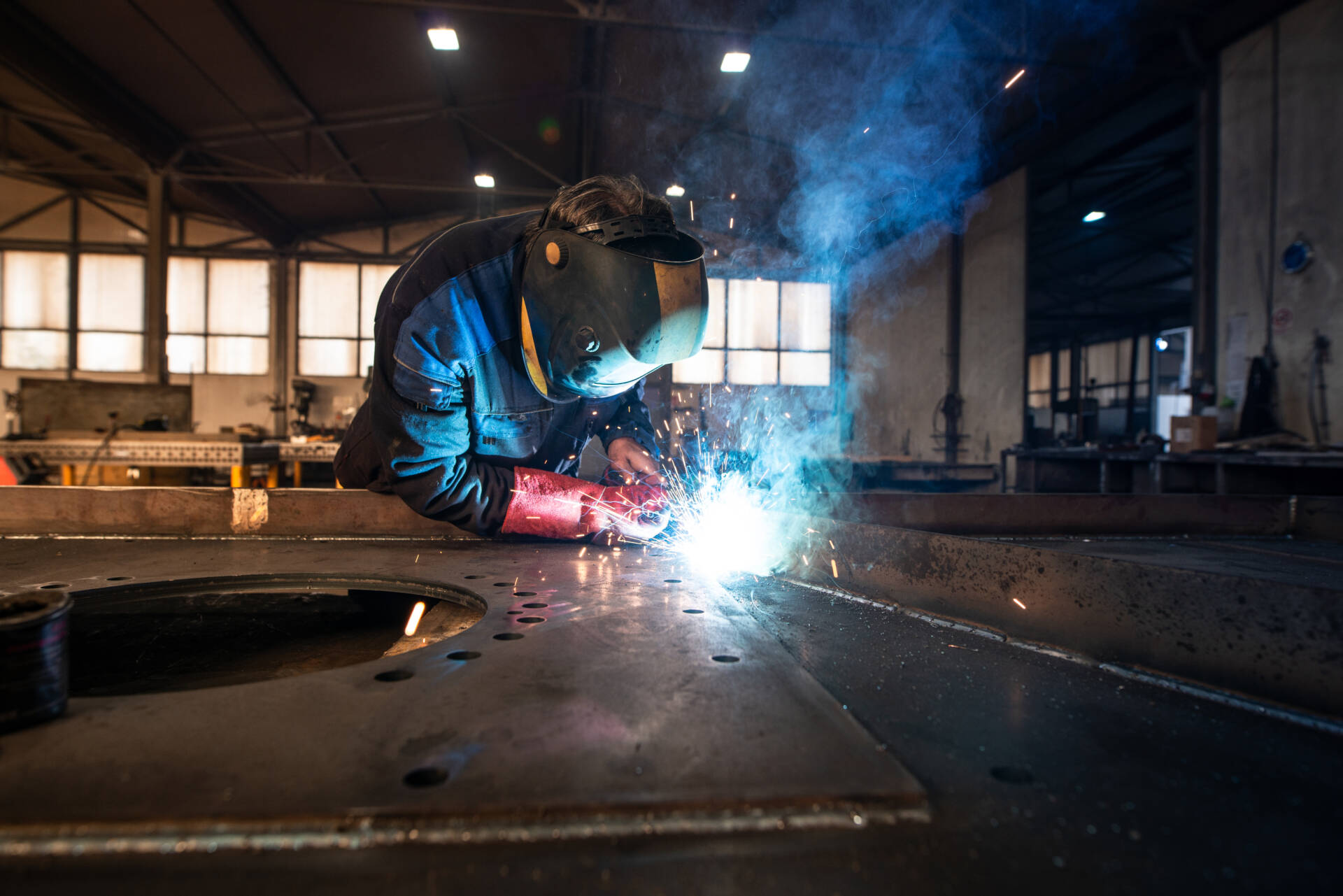

The welding industry is quickly expanding, owing to increased demand for combining different and non-metallic materials, the evolution of customized and unique shapes/designs, the introduction of various welding and cutting technologies, and many other factors. In such cases, the use of welding electrodes is increasing due to their capacity to provide high precision welding in real-time. Furthermore, advantages such as compact size, flexibility, and low spark incidence are contributing to the increasing deployment across diverse industries such as automotive, building & construction, and others. For example, the car industry is working hard to align its goods with environmental norms and standards, particularly CO2 emissions. Welding electrodes optimize the welding technique, eliminate waste, and increase production and efficiency at all levels.



