Project Report For Current Transformer
Introduction
Project Report for Current Transformer is as follows.
A current transformer is an instrument transformer that creates alternating current (AC) within the secondary winding of the transformer. This is also known as a series transformer since it is connected in series with the circuit for monitoring various electric power parameters. In this case, the secondary winding current is proportionate to the primary winding current. These are employed in the conversion of high-voltage currents to low-voltage currents.
Current transformers and voltage or potential transformers are examples of instrument transformers. Instrument transformers convert high voltages or currents into manageable, standardised values for instruments and safe relays. The instrument transformers disconnect the high voltage of the primary system from measurement or protective circuits.
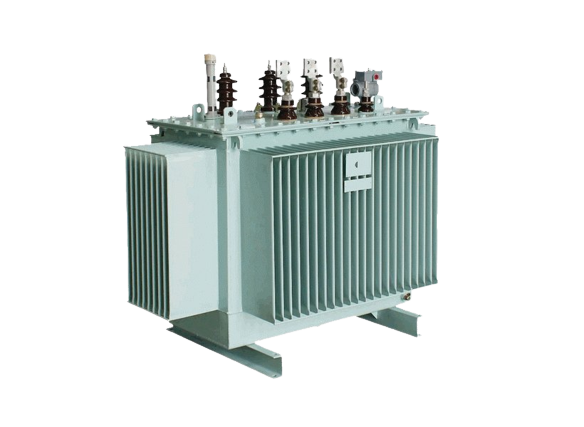

A current transformer delivers a secondary current that is precisely inversely proportional to the source current. The primary circuit is barely loaded by the current transformer. The power system’s current sensing components are current transformers. Electrical substations, producing stations, and the distribution of electric power in commercial and industrial settings all require current transformers.
When compared to a regular voltage transformer, the working principle of a current transformer is somewhat different. It has two windings, just like a voltage transformer. When alternating current is supplied through the main winding, alternating magnetic flux is formed, and alternating current is induced within the secondary winding. The load impedance is quite low in this type. As a result, this transformer operates in short circuit situations. So the current in the secondary winding is determined by the current in the main winding but is unaffected by the load impedance.
Construction of Current Transformers
Core :- To produce low magnetising ampere twists, the core material must have low iron losses and reluctance. Core materials such as nickel and an iron alloy have distinct features such as low loss and high permeability.
Windings :- The leakage reactance of the transformer can be minimised by placing the windings close together. Copper strips are used in the primary winding, whereas SWG wires are employed in the secondary winding. These windings can be built for suitable strength and fixed bracing without causing any harm.
Insulation :-The transformer windings are protected with varnish and tape. High voltage applications necessitate insulation systems that are absorbed by the oil used in the windings.
The core of the current transformer is made of silicon steel lamination. For producing cores with a high degree of accuracy, Permalloy or Mumetal used for the making of cores. The current to be measured is carried by the primary windings of the current transformers and is linked to the main circuit. The transformer’s secondary windings carry the current proportional to the current to be measured, and they are connected to the current windings of the meters or instruments.
Project Report Sample On
Current Transformer
Get Completely Custom Bankable Project Report
Raw Material Of Current Transformer
The basic raw material ‘Cold Rolled Grain Oriented (CRGO) Steel’ is used for both Lamination and Wound Cores. It is imported from respected international mills in Japan, Korea, Russia, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Brazil, and the United States in various permeability grades. CRGO Steel is available in a variety of grades, including M-3, M-4, M-5, and M-6, as well as HI-B. These raw materials are imported in the form of mother coils with widths of 750/1100 mm. CRGO material has the lowest maximum core loss value in the rolling direction.
The core loss at any given flux density increases as the shearing angle to the rolling direction increases, and it is often greatest in the transverse direction. As a result, CRGO can be used in static electrical equipment such as power transformers, distribution transformers, reactors, audio transformers, and current transformers.
CT cases are made of polycarbonate, which is flame retardant and non-drip and meets UL 94 V-0 standards. Polycarbonate is a very robust and lightweight engineering plastic material with mechanical qualities that are very close to those of metallic housing.
Market Potential Of Current Transformer
The size of the current transformer market exceeded USD 1.5 billion in 2021, and it is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of more than 7% between 2022 and 2030. The electrification of rural areas is gaining attention, which is anticipated to fuel industry expansion.
Expenses
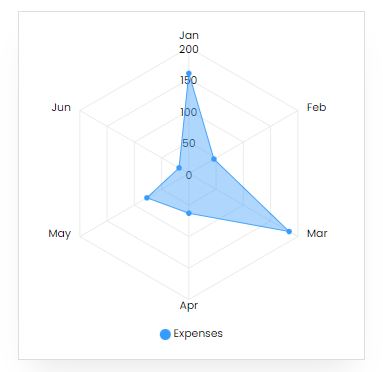
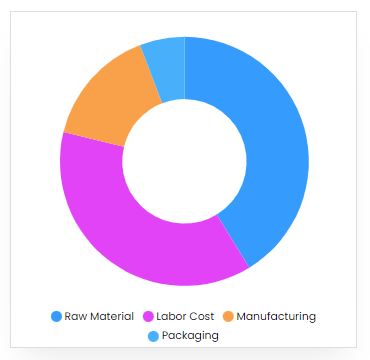
Product Cost Breakup
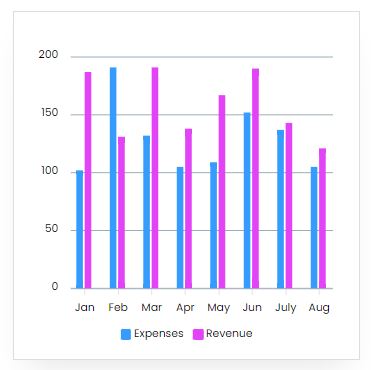
Reveneue Vs Expenses
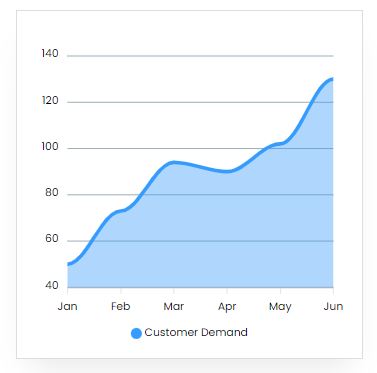
Market Trend
The Instrument Transformers business in India manufactures current transformers and voltage transformers with ratings ranging from 0.66 kV to 765 kV for both indoor and outdoor applications. The business also exports instrument transformers with indoor voltages up to 36 kV and outdoor voltages exceeding 12 kV.
Over the previous two years, the industry has also demonstrated its strength by creating a 1200 kV CVT for a 1200 kV test station. Because the need for equipment has often fallen over the last year, the industry’s situation has not improved. Even in the 400 kV category, as well as the 220/120 and 66 kV sectors, the market size was shown to be dropping.
The drop in the 765 kV segment was noticed, owing primarily to the transition from AIS to GIS. However, no serious threats were seen as a result of exports. Many surge arrester players have started manufacturing CTs in the new industrial scenario, and many players have entered the field with CTs up to 220 kV range.
Customers were also found strengthening quality standards and implementing severe quality acceptance criteria for these products.

