Project Report For Gravity Die Castings
Introduction
Project Report for Gravity Die Castings is as follows.
Castings created in metal moulds with a gravity head are referred to as “gravity die casting.” Casting in permanent moulds is the term used. For non-ferrous low melting temperature alloy pieces, such as those made of aluminium, zinc, magnesium, and copper alloys, gravity die casting is a reproducible casting technique. Die casting is a manufacturing process used to create metal parts with precise dimensions, clearly defined edges, and either smooth or textured surfaces. By pressing molten metal onto reusable metal dies, it is accomplished.
These die casting alloys play an important role due to their inherent and multidimensional features, such as their light weight, strength to weight ratio, corrosion resistance, electrical and thermal conductivity, and non-toxicity. In die cast parts, high strength alloys are gradually replacing steel and cast iron.
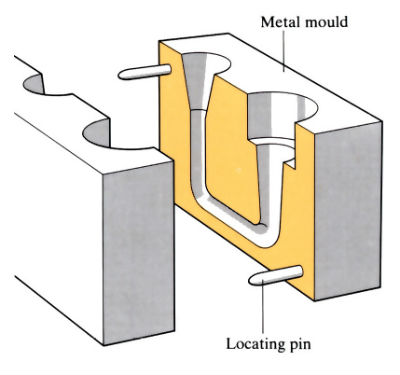
Product & Application of Gravity Die Castings
Gravity die cast components composed of zinc, copper, magnesium, and aluminium alloys are required for critical applications and mass-produced goods. The major materials used in hot chamber machines are zinc and low melting point alloys, which do not quickly attack and damage metal pots, cylinders, and plungers. Because of enhanced technology and the development of new, higher temperature materials, the applicability of this equipment for magnesium alloys has grown.
Gravity die casting is used to create parts for automobiles such as pump bodies, clutch housings, crank cases, gear box housings, and pistons. Die castings are used for a wide range of products, including ashtrays, water jugs, art metalwork, moulding flasks, core drying plates and pattern castings, ceiling fan rotors, storage tanks and fittings for chemical and marine uses, railway components, flywheel housing and propellers, artificial limbs, ornamental hardware in the building industry, and many other parts in numerous industries.
According to BIS, ASTM, and DIN specifications, diverse aluminium, zinc, and magnesium alloys are offered for a range of applications.
Project Report Sample On
Gravity Die Castings
Get Completely Custom Bankable Project Report
Raw Material For Gravity Die Castings
There is a need for aluminium alloys in a variety of grades, including LM-5, LM-6, LM-16, LM-24, etc. Likewise, alloys made of zinc and magnesium are also available. other consumables, such as lubricants, die coating, fluxes, ladle coatings, and mould release agents. Materials for surface treatment are also necessary.
Market Potential Of Gravity Die Casting
The market for die casting was valued at USD 55.47 billion in 2015, and by 2022, it is expected to reach USD 80 billion. From 2017 to 2022, the market is anticipated to expand at a CAGR of around 6.60%.
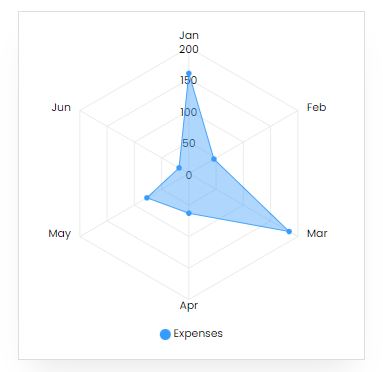
Expenses
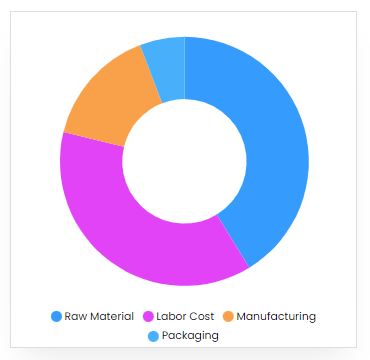
Product Cost Breakup
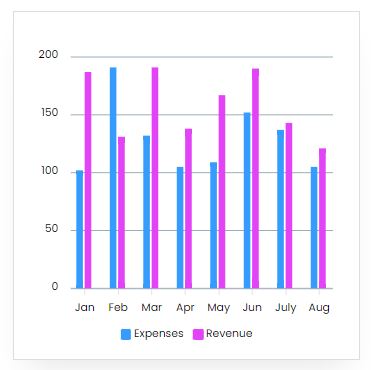
Reveneue Vs Expenses
Market Trend
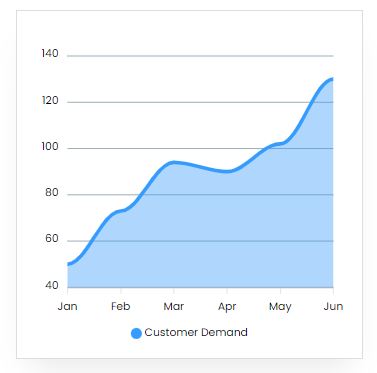
The market for die-end casting is quite diverse and well established in almost all industries, with steady increases in output, demand, and consumption. The market for die-casting magnesium, zinc, and other metals is predicted to grow at a quicker CAGR of 10.0% over the following five years.
The global market for die-castings for industrial applications is predicted to grow at a faster CAGR of 7.83% during the forecast period. Additionally, it is expected that the market for die-casting in electrical and electronic applications will grow gradually and make up 11% of the global die-casting industry by 2016.
India is becoming increasingly important as a centre for the production of die cast vehicle parts, notably those made of aluminium, magnesium, and zinc. India and China are anticipated to expand the global market, which will be significantly fueled by the automobile industry’s explosive rise. Die-greatest casting’s market is in Asia-Pacific, which accounted for more than 50% of the global market in 2015.
India’s liberal economic policy and ongoing reforms are a key driver of the country’s aluminium die casting industry’s expansion. The availability of a skilled labour force at a lower cost and government incentives for small and medium-sized businesses both contribute to this.
