Project Report For Pomegranate Cultivation
Introduction
Project report for Pomegranate Cultivation is as follows.
Pomegranate is a significant fruit crop native to arid and semi-arid parts of Iran. Arid regions are typified by high temperatures, irregular and infrequent rainfall, and frequent drought; soils are deficient in nutrients and water holding capacity.
Because the climatic circumstances in dry regions are very difficult for plant sustainability, selecting a fruit crop for such regions is critical for economic output. Pomegranate is commercially farmed in India’s Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, and Rajasthan state.
Sample Project Report Of Pomegranate Cultivation For Bank Loan
Get Completely Custom Bankable Project Report
India is a significant pomegranate grower, having the greatest area in the world. Pomegranate was planted on 2.16 lakh hectares in 2016-17, yielding 24.42 lakh tonnes with productivity of 11.70 tonnes/ha. Maharashtra is the top state, accounting for 65.51 percent of total pomegranate output and 64.61 percent of total area (Anonymous, 2017).
India is the only nation in the world that has pomegranates accessible year-round (January – December). Iran exports the most pomegranate (60,000 tonnes), followed by India (35,176 tonnes) (Chandra and Jadhav, 2009). Iran, India, China,
The United States are the world’s top producer, accounting for 76 percent of worldwide production. Additionally, it is cultivated for table and decorative use in Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Vietnam, Thailand, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, Armenia, Georgia, Morocco, Tunisia, Egypt, Israel, Syria, Lebanon, Greece, Cyprus, Italy, France, Spain, Portugal, Mexico, Argentina, and Chile.

However, due to the world’s constant growth, there is no precise statistics. In Rajasthan, it is primarily grown in the districts of Jaipur, Ajmer, Alwar, Tonk, Sriganganagar, Pali, Kota, Jalore, Banswara, Sawai Madhopur, Bhilwara, Jhunjhunu, Bikaner, and Sirohi on an area of 12,000 ha, with acreage in the Thar desert, specifically Barmer, Jodhpur, and Jaisalmer, increasing at Pomegranate is resistant to extreme climates and can weather heat, drought, and moisture deficiency.
Pomegranate farming is rising in India on a daily basis because of its great demand, hardiness, cheap maintenance cost, high yield, superior storage quality, and medicinal properties. It is very beneficial medicinally and nutritionally and is one of the greatest sources of antioxidants. Fruit is processed to create a variety of processed goods, including juices, squash, jelly, anardana, and mouth freshener.
The juice is very healthy and is advised for those experiencing stomach discomfort. Per 100 g fresh weight of fruit, it includes 67.95 kcal calories, 1.41 g protein, 1.60 g fibre, 2.50 mg calcium, 10.22 mg magnesium, 34.3 mg phosphorus, 0.39 mg iron, 0.26 mg zinc, 0.09 mg thymine, 0.22 mg niacin, 23.38 mg ascorbic acid, and 26.00 mg total carotenoids.
It has been used to treat sore throats, coughs, urinary infections, digestive problems, and skin conditions, and may help avoid heart disease, heart attacks, and strokes. Syphilis is treated with the seed, while jaundice and diarrhoea are treated with the juice. The flower’s juice is used to alleviate nosebleeds. The fruit pulp and seed are stomachic; dried, powdered flower buds are used as a bronchitis cure, and it is referred to as a “superfood” due to its multiple health and nutritional advantages.
Market Potential Of Pomegranate Cultivation
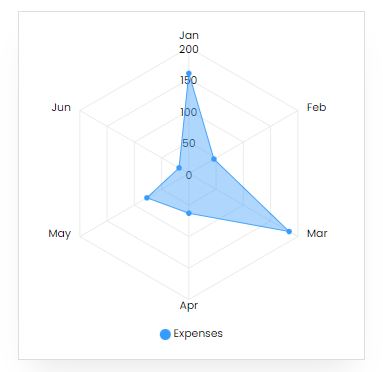
Expenses
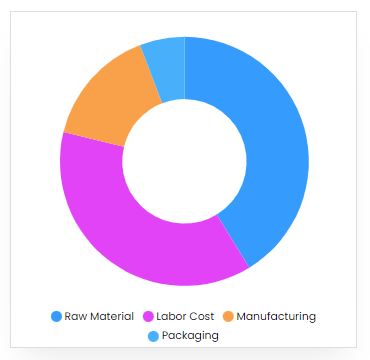
Product Cost Breakup
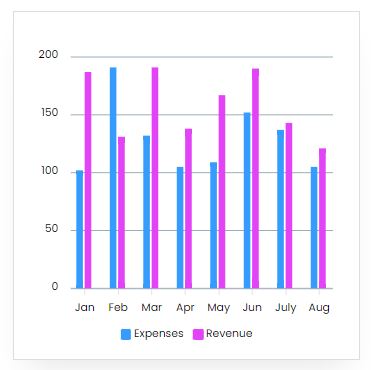
Reveneue Vs Expenses
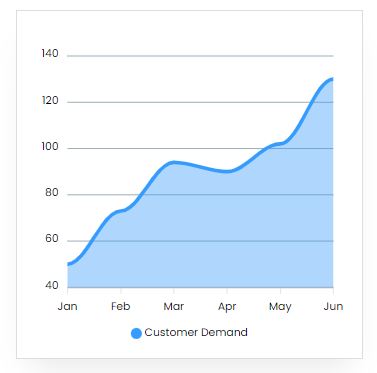
Market Trend
Pomegranate may be cultivated on a broad variety of soils from sandy soil to sandy loam soil. Light soil with a pH range of 6.5 to 7.0 is extremely appropriate for its growth; nevertheless, it can withstand pH up to 8.5 under good management measures.
Fruit quality and colour development are acceptable on light soils but poor in heavy soils. It tolerates salinity up to 6.00 DSM-1 and sodicity up to 6.78 ESP (Waskar, 2006). Pomegranate cultivation is effective in arid environments since it can tolerate dry temperature and poor soil conditions common in arid ecosystems.
It can grow successfully even on marginal sites with poor fertility and shallow depth. Arid soils are weak in organic matter and nutrient content, so good management of soil health, nutrient delivery is essential to produce a high yield.
Pomegranate has broader flexibility since it grows well in tropical, subtropical, desert and temperate environments because of its tough character. However, its principal cultivation is restricted to the northern hemisphere. Interestingly, the greatest quality fruits are grown in dry environments.
It grows as a deciduous shrub in the temperate zone but evergreen or partly deciduous in tropical and subtropical environments, which also relies upon the variety/ genotypes. It grows extremely well in the semi-arid area where chilly winter and scorching summer dominates. The tree demands warm and dry conditions during fruit growth and ripening.
The particular flexibility of pomegranate is visible from the threshold limit it shows for higher of 44°C and lower as -12°C temperature. Arid and semi-arid locations with annual rainfall 500 to 1000 mm with long, hot and dry summer and moderate winter are good for pomegranate growth. It can readily handle temperatures up to 45-48°C accompanied by dry hot breezes

