Project Report For Circuit Breakers
Introduction
Project report for circuit breakers is as follows.
All fuses need to be replaced with MCB for better safety and control when they have done their job in the past. An MCB, in contrast to a fuse, functions as an automated switch that opens in the case that the circuit receives an excessive amount of current.
Once the circuit returns to normal, it can then be closed again without the need for a manual replacement. In the majority of circuits, MCBs are generally employed as a fuse switch substitute. Today, a wide range of MCBs with breaking capacities ranging from 10 ka to 16 ka are used in all types of home, commercial, and industrial applications as a dependable form of protection.
A circuit breaker is an electrical switch that operates automatically and is intended to safeguard an electrical circuit against harm brought on by an overload or short circuit. Its fundamental job is to stop current flow when a defect is found.
To restart normal operation, a circuit breaker can be reset (manually or automatically), unlike a fuse, which can only be used once before needing to be replaced. There are many different sizes of circuit breakers, ranging from small devices that protect low-current circuits or specific home appliances to huge switchgear intended to safeguard high voltage lines supplying an entire city.
ADS is sometimes used to refer to the general purpose of a circuit breaker, RCD, or fuse as an automatic means of cutting power to a malfunctioning system (Automatic Disconnection of Supply).

Product & Application of Circuit Breakers
A micro circuit breaker, often known as an MCB, is an electromagnetic device that is entirely enclosed within a moulded insulating material. An MCB’s primary job is to automatically switch the circuit, or open the one that is linked to it, when the current flowing through it exceeds the limit for which it is set. If necessary, it can be manually turned ON and off like a regular switch.
The amount of an overcurrent that triggers an MCB determines how long it will operate for. This indicates that they are activated whenever an overload persists long enough to endanger the circuit they are intended to protect. As a result, transient loads like switch surges and motor starting currents are ignored by MCBs. These typically have operating times of less than 2.5 milliseconds for short circuit faults and 2 seconds to 2 minutes for overloads (depending on the level of current).
Different pole versions of MCBs, including single, double, triple, and four pole structures with various fault current levels, are produced. MCBs are typically connected to create two- and three-pole versions, which allow complete circuit isolation in the event of a fault in one line. In the event that the three phase motor protection only has one phase, this feature will be useful.
Project Report Sample On
Circuit Breakers
Get Completely Custom Bankable Project Report
Types of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers can be divided into a variety of categories based on characteristics including voltage class, construction type, interrupting type, and structural elements. circuit breakers for low voltage, Common trip breakers, thermal magnetic, magnetic-hydraulic, medium-voltage, and high-voltage circuit breakers are all types of magnetic circuit breakers. circuit breakers for high voltage made of sulphur hexafluoride (SF6), Disconnecting the circuit breaker (DCB), the high-voltage carbon dioxide (CO2) circuit, etc.
Market Potential Of Circuit Breakers
The market for circuit breakers was valued at USD 6.62 billion in 2016; by 2022, it is anticipated to have increased to USD 8.68 billion, with a CAGR of 4.85%.
The main factors that will propel expansion in the circuit breaker market include expanding access to energy in developing nations, rising building and development activities, and an increase in renewable power generation projects.
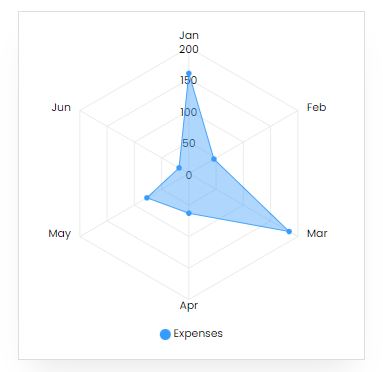
Expenses
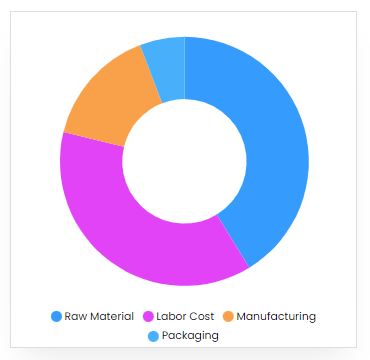
Product Cost Breakup
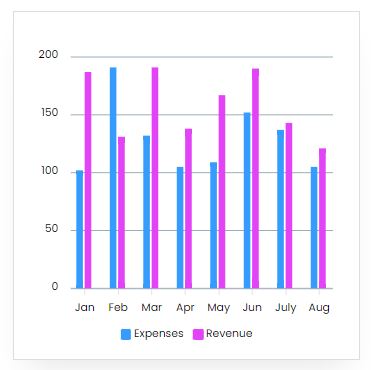
Reveneue Vs Expenses
Market Trend
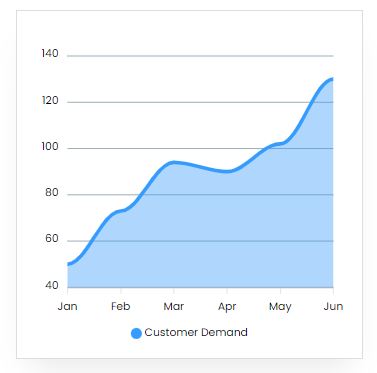
One of the main factors in the effective and consistent power supply is the circuit breakers. Circuit breakers are in high demand in India due to a growing emphasis on the efficient transmission and distribution of power as well as ongoing demand from end-user industries.
As a result of the Indian government’s goal to increase electricity capacity by 88,536 MW (Mega Watt) throughout the course of the 12th year plan, or from 2012 to 2017, high voltage circuit breakers have become more prevalent in high power transmission and sub-transmission projects.
The revenues from the Indian circuit breaker market are anticipated to increase between 2013 and 2018 at a CAGR of almost 15%, according to “India Circuit Breakers Market Forecast & Opportunities, 2018”. Low voltage circuit breakers currently rule the market.
Due to the increased demand from low voltage segments, it is predicted that MCB and MCCB will account for more than 30% of revenue share by 2018. Schneider Electric, Siemens, L&T, and ABB are the top companies active in the Indian circuit breaker market.

