Project Report For Pea Farming
Introduction
Project report for pea farming is as follows.
The pea, or Pisum sativum, often known as garden pea, is a herbaceous annual plant in the Fabaceae family that is practically grown everywhere for its tasty seeds. Fresh, canned, or frozen peas are all readily available, and dried peas are frequently used in soups.
The edible pods of some kinds, such as sugar peas and snow peas, are consumed raw or cooked like green beans and are commonly used in East Asian cuisines. The seeds are a good source of protein and dietary fibre, and the plants are not too difficult to grow.
Pea farming in India is an important agricultural activity that plays a vital role in the country’s economy. Peas, also known as green peas or garden peas, are a type of legume that are grown for their seeds, which are typically consumed as a vegetable. In India, peas are grown in a variety of regions, with the major production areas being in the states of Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Bihar, and Rajasthan.

Pea farming in India has a long history, with the crop being cultivated in the country for centuries. Peas are a hardy and adaptable crop that can be grown in a variety of soil types and climates, making them well-suited to cultivation in India.
In recent years, the demand for peas in India has increased significantly, driven by rising population and incomes, as well as the growing popularity of western-style cuisines that feature peas as a key ingredient.
Pea farming in India is typically done on a small scale, with most farmers cultivating the crop on small plots of land using traditional techniques. However, in recent years, there has been a trend toward the adoption of modern farming techniques, such as the use of improved seed varieties, chemical fertilizers, and irrigation systems. These techniques have helped to increase productivity and reduce the risk of crop failure, but have also led to concerns about the environmental impact of pea farming in India.
Get Completely Custom Bankable Project Report
There are opportunities for exports of peas from India. India is a major exporter of peas, with significant exports to countries in Asia, Europe, and the Middle East. There is also potential for exporting value-added pea products, such as pea protein and pea starch, to countries around the world.
Market Potential Of Pea Farming
The pea processing industry is expected to earn USD 5.0 billion in sales by 2026, at a CAGR of 10.1%. The industry is expected to be worth USD 3.1 billion in 2021.
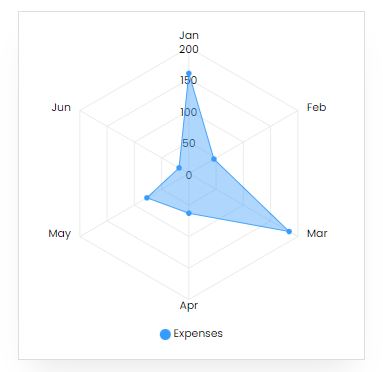
Expenses
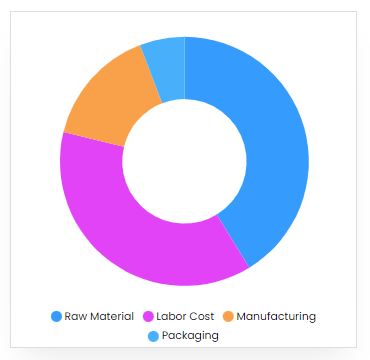
Product Cost Breakup
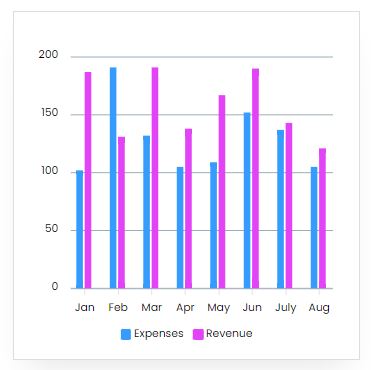
Reveneue Vs Expenses
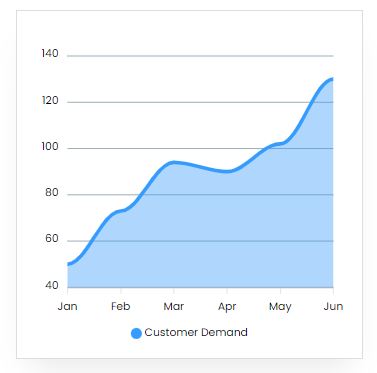
Market Trend
Pea farming in India has significant potential as a profitable and sustainable agricultural enterprise. India is the world’s second-largest producer of peas, with an annual production of around 4.5 million metric tons. Peas are an important source of protein, fiber, and various essential nutrients, and are widely consumed in India and around the world.
There are several reasons why pea farming in India holds significant market potential. First, there is strong domestic demand for peas. Peas are a staple in many Indian dishes, such as aloo matar (peas and potatoes) and chana masala (chickpeas and peas), and are also used as an ingredient in snack foods such as bhujia and sev. In addition, there is a growing demand for frozen and canned peas, as well as for pea protein and pea starch, which are used in a variety of food and non-food products.
Second, India has a favorable climate and soil conditions for pea cultivation. Peas are a cool-season crop that can be grown in a wide range of soil types, including loamy, sandy, and clay soils. They are also relatively drought-tolerant, making them well-suited for dryland farming in many parts of India.
Third, there are several government initiatives in place to support pea farming in India. The National Food Security Mission (NFSM), for example, aims to increase the production of pulses (including peas) by providing financial assistance to farmers for seeds, fertilizers, and other inputs. The National Horticulture Mission (NHM) also provides assistance to farmers for the cultivation of horticultural crops, including peas.
