What actually is ITR?
The income tax return is the form on which an assessee reports information about his or her income and taxes with the Income Tax Department. ITR 1, ITR 2, ITR 3, ITR 4, ITR 5, ITR 6, and ITR 7 are all different types. If you submit a late return, some losses cannot be carried forward.
The Income Tax Act of 1961 and the Income Tax Rules of 1962 assist citizens in filing annual returns with the Income Tax Department. These returns must be filed by the due date mentioned. Every Income Tax Return Form is only applicable to a subset of Assessees.
The Income Tax Department of India only processes Forms filed by eligible Assessees. It is so critical to understand which form is appropriate in each situation. Income Tax Return Forms differ according to the Assessee’s source of income and category.
- Which ITR Should You Submit?
Let us determine the appropriate type of ITR form based on your tax profile, income source, and amount. The several types of ITR forms and their applicability are shown below.
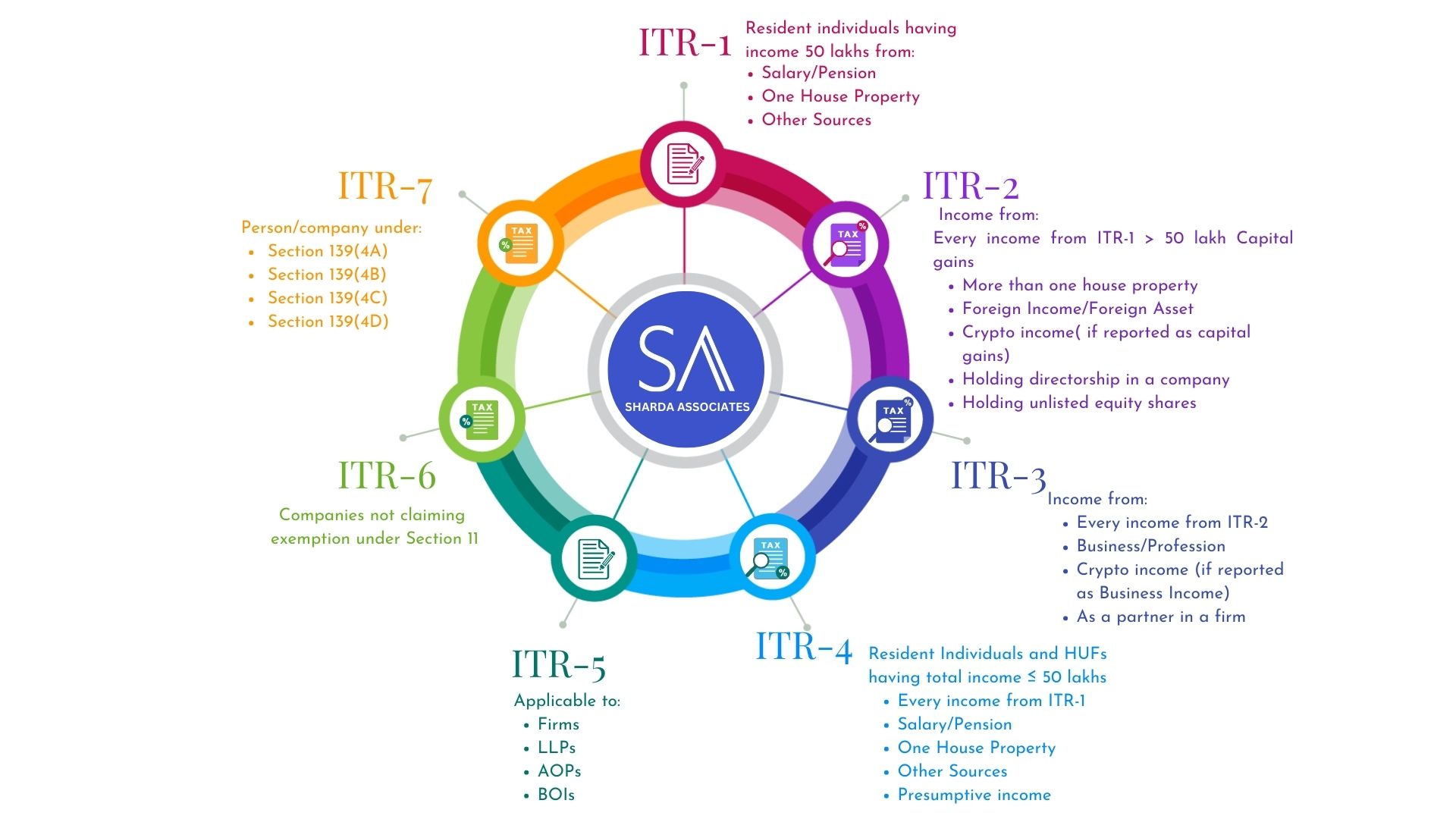
- ITR-1
If you are an individual resident obtaining income from salary/pension, one house, and other sources, including agriculture income, the ITR-1 form applies to you. In this instance, your total annual income should not be more than Rs. 50 lakh.
- ITR -2
If your total income from all sources included in ITR-1 exceeds Rs. 50 lakh, you must file ITR-2.
You are a corporate director; you own unlisted equity shares; you have received income as capital gains; you have international assets or foreign income sources; and agricultural revenue in excess of Rs. 5,000.
- ITR -3
If you own a business or are a professional, you should utilize the ITR-3 form to file your income taxes. This sort of ITR is also relevant if you are an individual director in a company and own unlisted shares in that firm.
Income from house property, salary, pension, as a partner in a firm, and other sources should also be included in the income tax return file.
- ITR-4
Individuals, HUFs, and partnership firms (excluding LLPs) residing in India with a total income of up to Rs.50 lakhs and income from business and profession estimated under sections 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE utilise the ITR-4 or SUGAM form.
- ITR-5
Limited Liability Partnerships (LLPs), Artificial Juridical Persons (AJPs), Associations of Persons (AOPs), and Bodies of Individuals (BOIs) are all covered by ITR-5. Investment funds, business trusts, and estates of the deceased and insolvent also adopt this form.
- ITR-6
ITR-6 must be filed online and applies to all other businesses other than above except those exempt under Section 11 of the Income Tax Act of 1961.
- ITR-7
Charitable trusts, political parties, religious organisations, news organisations, scientific research societies, universities, colleges, and hospitals are all covered under ITR-7.
Conclusion
The right Income Tax Return (ITR) form to file is determined by a variety of circumstances, including the nature of your income, residential status, and financial activity. It is critical to choose the correct ITR form because submitting the incorrect form may result in penalties or legal difficulties.
Assess your income sources, such as salary, company revenue, capital gains, or property income, carefully to decide the suitable form. Take into account your residency status, whether you are a resident or a non-resident. In addition, evaluate the tax authorities’ unique eligibility conditions and instructions. Consultation with a tax professional or use of the official tax website will help guarantee that you file the correct ITR form and fulfil your tax obligations correctly.



