Ratio analysis is the method of evaluating financial ratios which are required to reflect a firm’s current financial output utilizing a few different forms of ratios like liquidity, profitability, activity, and debt ratios.
Or, In order to measure a firm’s financial fitness. The values often used to measure a firm’s financial ratios are derived from the firm’s financial statements.
There are 6 types of Ratio Analysis
- Liquidity Ratios
- Profitability Ratios
- Solvency Ratios
- Turnover Ratios
- Earnings Ratio

Liquidity Ratios
This type of ratio aids in determining a business’s capacity to meet its short debt obligations. A stronger liquidity ratio indicates that the business is good at making cash.
Liquidity ratios can be classified into the following categories: –
Must Read – What is Liquidity Ratio?
- Current Ratio:
The current ratio is the ratio of a firm’s current assets to current liabilities. The current ratio is designed to determine a firm’s ability to fulfil its debt obligations for the next 12 months. A stronger current ratio indicates that the firm is well-positioned to meet its short-term debt obligations.
The quick ratio is used to determine a firm’s capacity to pay off its current liabilities in the shortest amount of time.
This form of ratio assists in assessing a firm’s capabilities to attain adequate income.
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
- Quick Ratio:
The quick ratio is used to determine a firm’s capacity to pay off its current liabilities in the shortest amount of time.
This form of ratio assists in assessing a firm’s capabilities to attain adequate income.
Quick Ratio = (Cash and Cash Equivalents + Marketable Securities + Accounts Receivables) / Current Liabilities
Profitability Ratios
This form of ratio assists in assessing a firm’s capabilities to attain adequate income.
The given below are some examples of profitability ratios: –
Must Read – What is Profitability Ratio?
- Gross Profit Ratios:
GP ratios are determined to reflect a firm’s operating profits by rendering certain adjustments to COGS, or cost of goods sold.
Gross Profit Ratio = (Gross Profit / Net Sales) x 100
- Net Profit Ratio:
Net profit ratios are used to measure a firm’s total productivity by deducting all cash and non-cash expenses.
Net Profit Ratio = (Net Profit / Net Sales) x 100
- Operating Profit Ratio:
The operating profit ratio is intended to measure a firm’s financial strength and willingness to pay both short & long-term debt obligations.
Operating Profit Ratio = (Earnings Before Interest and Taxes / Net Sales) * 100
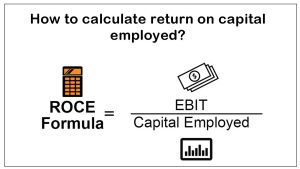
- Return on Capital Employed (ROCE):
Return on capital employed is intended to measure a firm’s profitability in relation to the money spent in the business.
Return on Capital Employed = Earnings Before Interest and Taxes / Capital Employed
Solvency Ratios
Solvency ratios are a form of ratio which is needed to calculate if a business is solvent and worthy of repaying its debt obligations.
Must Read – What is Solvency Ratio?
The given below are examples of solvency ratios: –
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio:
The debt-equity ratio is described as the ratio of total debt to shareholders’ funds. The D/E ratio is used to assess a firm’s leverage. A company’s optimal debt-equity ratio is 2:1.
Debt Equity Ratio = Total Debts / Shareholders Fund
- Interest Coverage Ratio:
The interest coverage ratio is intended to calculate a company’s solvency in the coming years, and also how many times the income received by that organisation is capable of matching its interest-related expenditures.
Interest Coverage Ratio = Earnings Before Interest and Taxes / Interest Expense
Turnover Ratios
Turnover ratios are used to calculate how successfully a firm’s financial assets & liabilities were utilized to raise profits
Must Read – What is Turnover Ratio?
The given below are examples of turnover ratios: –
- Fixed Asset Turnover Ratios:
The fixed assets turnover ratio is utilized to measure a firm’s performance in extracting income from its fixed assets.
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio = Net Sales / Average Fixed Assets
- Inventory Turnover Ratio:
The inventory turnover ratio is used to measure how rapidly a business turns its stocks into sales.
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost of Goods Sold / Average Inventories
- Receivable Turnover Ratio:
The receivable turnover ratio is used to measure a firm’s ability in accumulating or realizing its account receivables.
Receivables Turnover Ratio = Net Credit Sales / Average Receivables
Earnings Ratio
The earnings ratio is used to calculate the profits that a company makes for its investors.
The given below are examples of earnings ratios: –
- Profit Earnings Ratio:
The profit-earning capability of the organisation is shown by the P/E ratio.
Profit Earnings Ratio = Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share
- Earnings per Share (EPS):
EPS denotes an equity holder’s profits based on a single stock.
EPS = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) / (Weighted Average of Outstanding Shares)
Ratio analysis serves as the foundation for financial analysis. Ratio analysis is often seen by financial statement readers to get a deeper view of a firm’s health.